Summary
Do you remember singing “And Bingo Was His Name-O!” when you were younger? This song was how you learned how to spell the farmer’s dog’s name. In this activity we will be using the Bingo game to learn about new career options! Learning about various careers now will help you decide which one interests you. Even if you already know what you want to be when you grow up, learning about career paths will help you plan your future.
Overview
Virtual Career Expos are a great way for you to explore a variety of interesting careers and learn about your career options. The K20 Center’s GEAR UP program works with professional volunteers who share their career stories and answer students’ questions. These career talks can help inspire you and help you get to know more about a particular career.
Snapshot
Engage
Explore
Explain
Extend
Evaluate
Materials List
Student Guide (optional; attached)
Premade Bingo Cards (attached)
Fill in the Blank Activity (optional; attached)
Writing utensils
What To Do
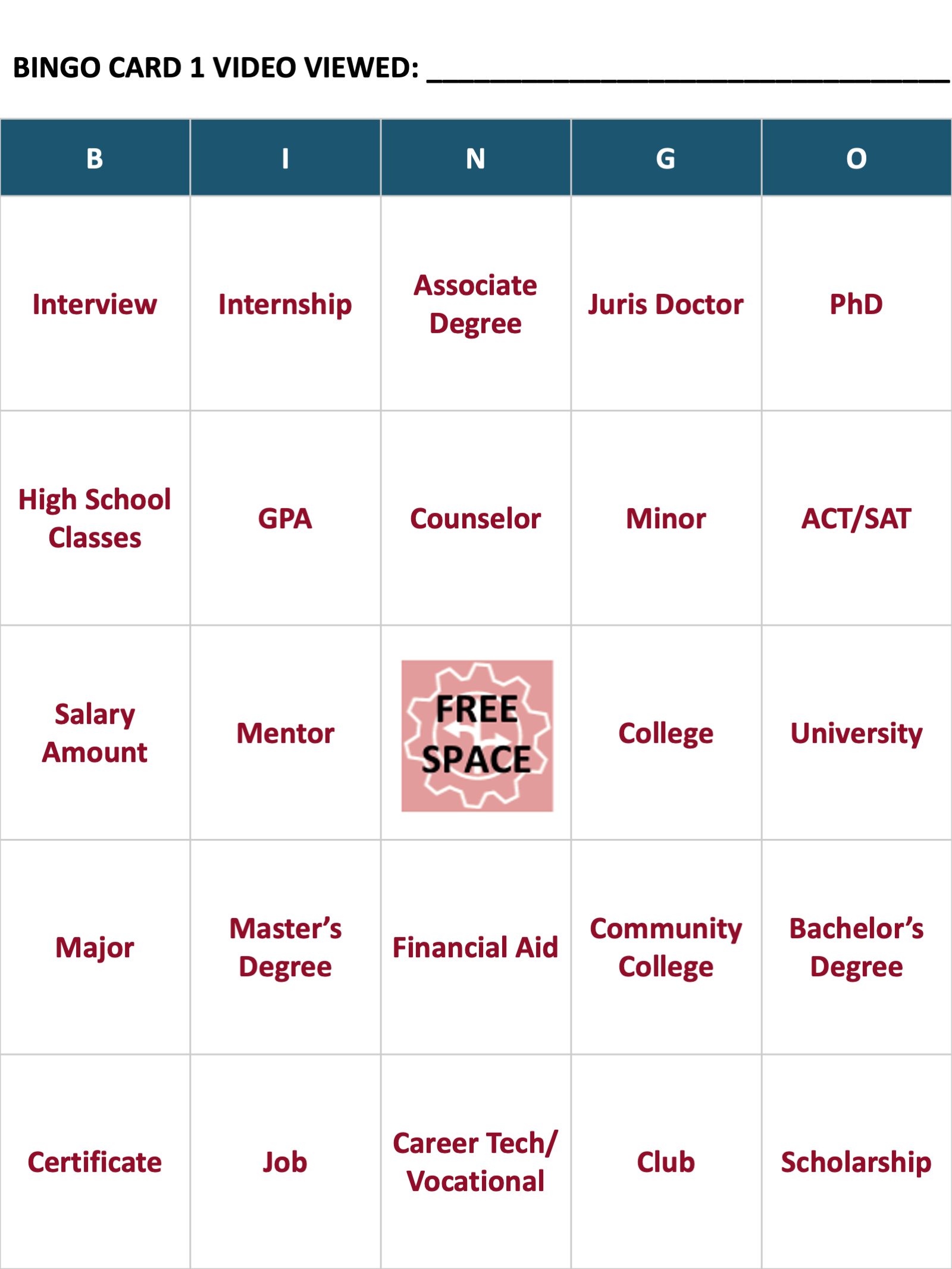
Open the attached Premade Bingo Cards packet. Follow the directions on page 1 of the packet to open the cards on your computer or print them out. (Ask a family member for help if you are not sure how to do this step.)
Review the list of terms and their definitions.
Choose a career video that you’d like to watch.
Choose one of the five Bingo cards (pages 2-6), and write the title of your video at the top of your Bingo card. See below for an example Bingo card.
Spend 1-2 minutes familiarizing yourself with the terms on the card.
Watch the video. While you are watching the video, listen carefully, and if you hear a word mentioned that’s on your card, mark it off. (You may want to pause the video at different times to check that you have marked off the terms.)
You can earn a Bingo by completing a line, a "T," a "U," a square, or a blackout.
When the video is over, review the definitions of the terms that you marked off.
Reflect on the video and activity by completing the 3-2-1 writing activity under the card (see below).

Alternate Bingo Activity
Open the attached Fill in the Blank activity packet. Notice the blank Bingo card on page 2 (see below).
Review the list of terms and their definitions on pages 3-5 of the packet (or at the bottom of this page).
Copy and paste a term of your choice into each square of the blank Bingo card.
Print out your custom Bingo card. (Ask a family member for help if you are not sure how to do this step.)
Choose a career video that you’d like to watch and write the title of the video above your Bingo card.
Spend 1–2 minutes familiarizing yourself with the terms on your board.
While you are watching the video, listen carefully, and if you hear a word mentioned that’s on your card, mark it off. (You may want to pause the video at different times to check that you have marked off the terms.)
You can earn a Bingo by completing lines, "T’s," "U’s," squares, or a blackout.
When the video is over, review the definitions of the terms that you marked off.
Reflect on the video and activity by completing a 3-2-1 writing activity.


Definitions
ACT/SAT: These letters are acronyms for American College Testing and the Scholastic Aptitude Test. Both tests are designed to measure a student's level of knowledge in basic areas such as math, science, English, and social studies. Colleges may require the results of either the ACT or SAT before granting admission.
Associate Degree: An undergraduate degree that you can earn after about two years from a junior or community college.
Bachelor’s Degree: An undergraduate degree that you can earn from a college or university after about 4 years of study.
Career Tech/Vocational: This postsecondary option focuses on specialized career training that prepares students for specific careers.
Certificate: Awarded after completing a training program at a technical or vocational center. The certificate is required to legally be able to work in the profession for which the training was received.
Club: An association or organization at your school that is dedicated to a particular interest or activity.
College: An establishment that offers higher education.
Community College: A two-year college that offers certificates and associate degrees. These colleges are a more affordable option compared to universities. Students who graduate with an associate degree can transfer to a public or private university to complete coursework for a bachelor's degree.
Counselor: Counselors assist with career exploration, personal development, academic challenges and short-term personal counseling. They can also refer you to community agencies.
Creativity: Using imagination to create ideas or produce artistic work.
Employability: Having skills needed for a job.
FAFSA: Students getting ready for college or attending college complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) to see if they qualify for financial assistance for college.
Financial Aid: Money that is given or lent to students in order to help pay for their education.
GPA: A student's GPA, or grade point average, is the equivalent of his or her average for curriculum course work. Each letter grade has an equivalent point value: A = 4 points, B = 3 points, C = 2, D = 1, and F = 0. A student may determine the grade points for each course by multiplying the number of points a grade is worth times the number of credits the course carries. Thus, a "B" grade, worth three points, in a three-credit course is worth nine grade points; an "A" grade in the same three-credit course is worth 12 grade points. The grade point average is found by adding the total grade point values for all courses and dividing by the total number of credits attempted during the same period of time.
High School Classes: Any class that a student will be or is taking in high school. These will help decide if a student likes certain components or skills needed in a career.
Internship: A position, typically without pay, for students to work within an organization or company. This allows students to gain experience or necessary qualifications they can later use to be considered for paying positions.
Interview: A formal meeting in which a person meets with a potential employer to help determine the person’s qualifications for the job.
Job: A paid position. Jobs require completing tasks for pay.
Job Security: Describes a job that is protected or one for which it is unlikely that the person holding it will lose the job. A person has job security when they work a job that is secure and likely to remain necessary or in demand.
Juris Doctor: A graduate degree in law.
Major: A major is a student's chosen field of study. It usually requires the successful completion of a specified number of credit hours.
Master’s Degree: A graduate-level degree that allows you to focus on and master a specific subject area. It takes, on average, two years to complete. You usually must have completed coursework on the bachelor's degree level prior to being accepted into a master's program.
Mentor: Someone who has experience in a certain area and advises someone else.
Minor: A minor (as opposed to a major) is designated as a specific number of credit hours in a secondary field of study.
PhD: The highest level of degree that students can earn. PhDs are considered experts in their field of study. On average, it takes an additional four to eight years to complete this graduate level of study.
Postsecondary Education: Postsecondary Education (PSE) refers to education after high school. This could include college or career tech/vocational.
Resume: An overview of a person’s education, qualifications, and previous experience that is sent with a job application.
Salary: An annual (yearly) amount of money that an employee makes.
Scholarship: A sum of money that is used to support a student's education, usually awarded for academic achievement. It can also be earned in other forms, such as athletics.
University: A higher education institution that offers a 4-year degree, as well as postgraduate degrees (Master’s, PhD, etc.).
Volunteer: A person who willingly helps with a service without being forced or paid to do it.
Resources
K20 Center. (n.d.). 3-2-1. Strategies. https://learn.k20center.ou.edu/strategy/117



