Summary
This collection is a series of five lessons about diffraction of light and sound. In Lesson 1, students will learn that light is formed by waves and can change direction through diffraction. They will use pencils to build a spectroscope and make observations as to the color and size of light. Students will then research wave diffraction and use what they learned to build and test a spectroscope. In Lesson 2, students will watch a video of fireworks and write down what they notice and wonder. Then, students will participate in a flame test lab and will draw Bohr models for the element hydrogen, labeled with arrows to show the release and absorption of energy. Finally, students will research the science behind fireworks and how it relates to an electron’s energy. In Lesson 3, students will explore the Doppler effect. They will practice by using a Doppler ball and the Doppler equation. Students will also learn how the Doppler effect is useful in our everyday lives with sirens and weather prediction. In lesson 4, students will learn that electrons in atoms and molecules absorb visible light. Students will perform two investigations into how various media absorb and transmit light and complete two guided inquiry model group activities. In the final lesson, lesson 5, students will apply the Doppler Effect to electromagnetic waves, and examine redshift as evidence of the expanding universe.Resources

Students will learn that light is formed by waves and can change direction through diffraction. They will use pencils to build a spectroscope and make observations as to the color and size of light. Students will research wave diffraction and use what they learned to build and test a spectroscope. Read more »
Diffraction Unit, Lesson 1: Bending Light
What Is Diffraction?
- National Science Foundation (NSF)
- 9th - Secondary
- Science
- Chemistry, Physics
- HS-PS4-3, CH.PS4.3 , PH.PS4.3 , SIN502, EMI201, EMI503

Diffraction Unit, Lesson 2: Funky Flames
Using Flame Tests to Explore Electrons' Energy Levels
- 9th - 12th
In this lesson, students will watch a video of fireworks and write down what they notice and wonder. Students will participate in a flame test lab. They then will draw Bohr models for the element hydrogen, labeled with arrows to show the release and absorption of energy. Finally, students will research... Read more »
Diffraction Unit, Lesson 2: Funky Flames
Using Flame Tests to Explore Electrons' Energy Levels
- National Science Foundation (NSF)
- 9th - 12th
- Science
- Chemistry, Physics
- HS-PS1, HS-PS1-1, CH.PS1.1 , CH.PS1.1.1, CH.PS1.1.2, IOD403, IOD404, SIN301, SIN303, SIN401, SIN403, SIN502, SIN503, EMI201, EMI301, EMI302, EMI403
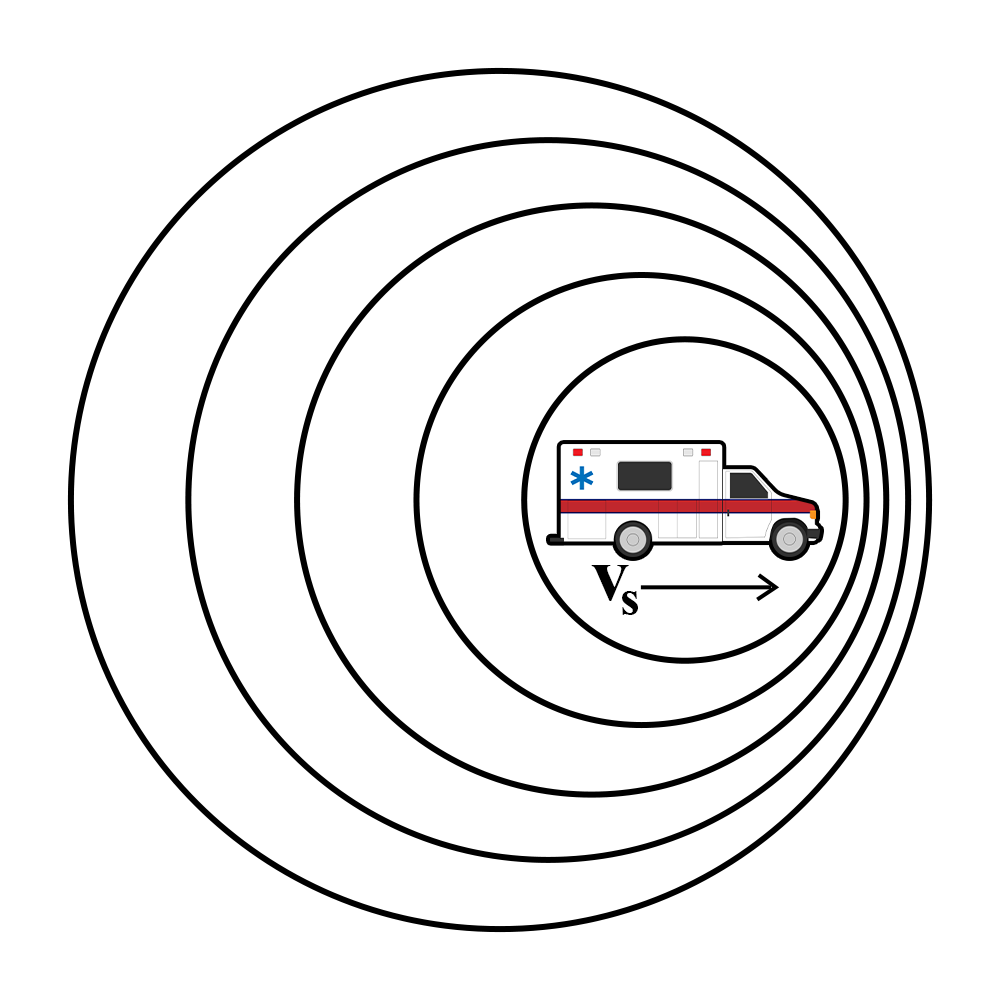
In this lesson, students will explore the Doppler effect. They will practice by using a Doppler ball and the Doppler equation. Students will also learn how the Doppler effect is useful in our everyday lives with sirens and weather prediction. Read more »
Diffraction Unit, Lesson 3: Wonky Waves
The Doppler Effect
- National Science Foundation (NSF)
- 9th - 12th
- Science
- Chemistry, Physics
- PH.PS4.1 , IOD304, IOD403, IOD404, IOD504, SIN301, SIN401
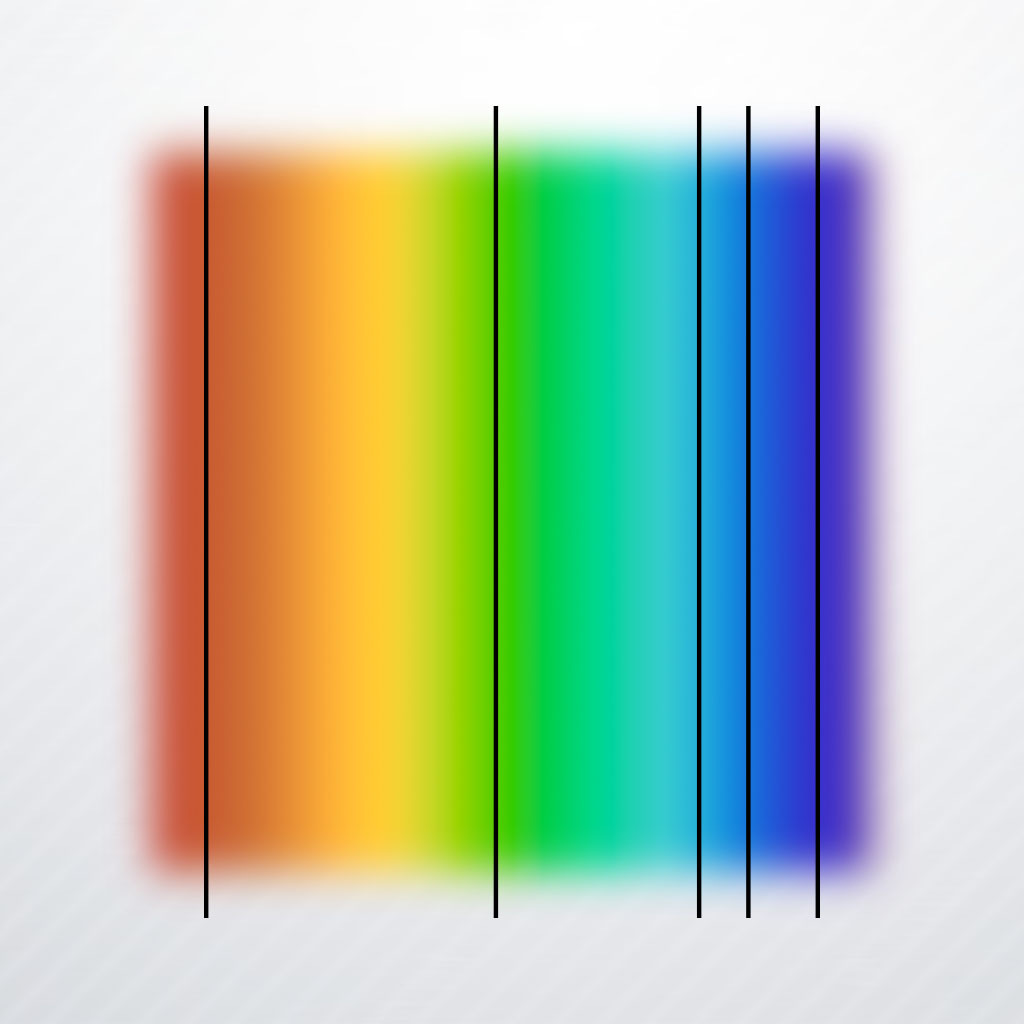
In this unit, students will learn that electrons in atoms and molecules absorb visible light. When light passes through various media and then through a diffraction gradient, it produces absorbance spectra. The produced absorption spectra are unique to the elements that interact with the light. These... Read more »
Diffraction Unit, Lesson 4; Missing Colors
Absorption Spectra
- National Science Foundation (NSF)
- 9th - 12th
- Science
- Physics
- PS.PS2, PS.PS1.1.1, PS.PS1.1.2, PS.PS4.1 , PS.PS4.1.1, CH.PS4.3 , IOD304, IOD403, IOD404, SIN201, SIN301, EMI301, EMI401, EMI502, EMI505
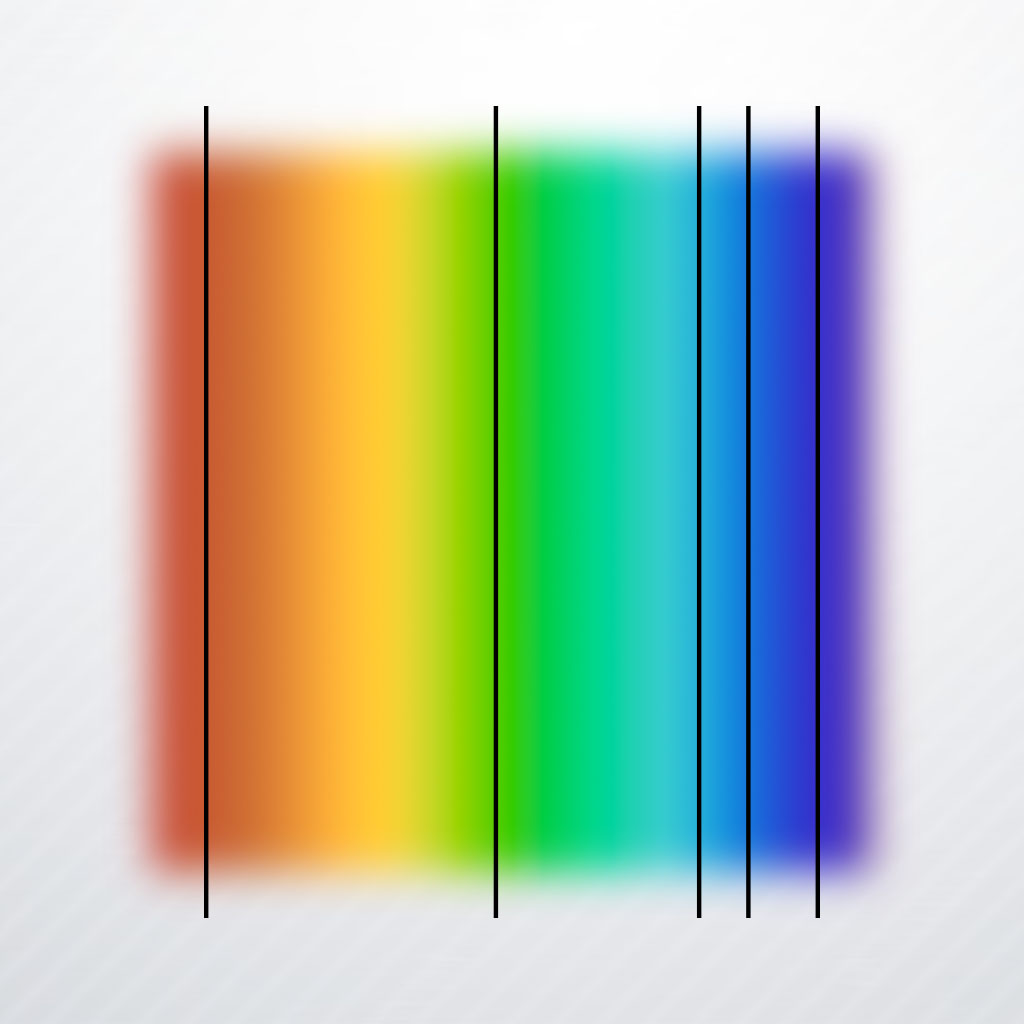
This is the fifth and final lesson in the Diffraction Unit. In this lesson, students will apply the Doppler Effect to electromagnetic waves, and examine redshift as evidence of the expanding universe. Read more »
Diffraction Unit, Lesson 5: The Red Universe
Redshift and the Expanding Universe
- 10th - 12th
- Science
- Physics
- HS-ESS1-2, CH.PS4.3 , PH.PS4.1 , PH.PS4.5
Standards
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons CC BY-SA 4.0 License.
Report copyright infringement »

